On November 3, 2023, the Minister of Public Works and Housing ("MOPWH") issued MOPWH Regulation No. 10 of 2023 on Smart Buildings ("Regulation 10/2023").
Regulation 10/2023 provides the guidelines and standards for building construction in order to ensure the sustainability of natural resources and reduce the impact of climate change through the concept of implementing smart buildings in accordance with the provisions of Government Regulation No. 16 of 2021 on Implementation of Law No. 28 of 2002 on Buildings and Presidential Regulation No. 63 of 2022 on the Detailed Master Plan of Nusantara Capital City.
Regulation 10/2023 defines a Smart Building as a Green Building that implements smart building management systems that are responsive to regional context, environment, local wisdom, and user needs that meet building technical standards and security systems using integrated high technology and work automatically in accordance with the principles of sustainability, function, and classification in each stage of their implementation.
Further, Green Buildings are buildings that meet building technical standards and have significant measurable performance in saving energy, water, and other resources through the application of Green Buildings principles in accordance with the function and classification at each stage of their implementation.
As provided in the purpose and definition of Smart Buildings above, Regulation 10/2023 is in fact issued to support the implementation of Green Buildings through technology and to support the development and construction of Green (and Smart) Buildings in Indonesia's new capital (i.e., Nusantara Capital or Ibukota Nusantara).
Further, Regulation 10/2023 regulates the technical standards, implementation, evaluation, certification, funding, development, and incentives and administrative sanctions of Smart Buildings.
We further elaborate on three aspects of Smart Buildings regulated in Regulation 10/2023, namely, technical standards, implementation, and incentives and administrative sanction below.
- Technical Standards of Smart Buildings
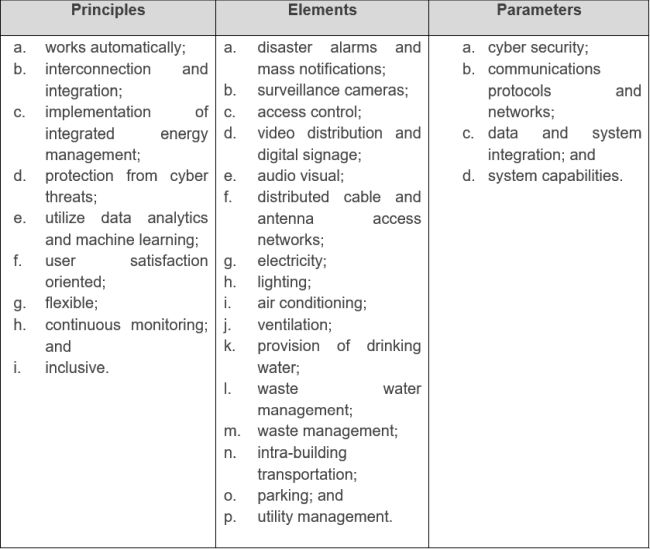
Article 3 of Regulation 10/2023 provides that every Smart Building shall meet the Smart Buildings technical standards according to its function and classification. Further, the technical standards of Smart Buildings under Regulation 10/2023, among others, the principles, elements, and parameters of Smart Buildings.
The principles of Smart Buildings are the principles that are taken into consideration in the realization of Smart Buildings at every stage of Smart Buildings implementation. The elements of Smart Buildings are components of a system or features in the Smart Buildings that utilize high technology integrated with the building management system of Smart Buildings. The parameters of Smart Buildings are the benchmark for assessing the elements of Smart Buildings in implementing the principles of Smart Buildings.
Following are the principles, elements, and parameters of Smart Buildings:
- Implementation of Smart Buildings
Smart Buildings shall be operated with consideration of the fulfillment of human, environmental, and technological aspects, as stated in the Smart Buildings principles. Further, the implementation of Smart Buildings must comply with the provisions of the Smart Buildings technical standards at each stage of its implementation.
Smart Buildings technical standards apply to new buildings and existing buildings based on the following categories:
- mandatory;
- recommended; and
- voluntary
The implementation of Smart Buildings is carried out in phases, namely, (i) programming; (ii) technical planning; (iii) construction; (iv) utilization; and (v) demolition. For the implementation of Smart Buildings by construction service providers shall involve Smart Buildings experts.
- Incentives for Smart Buildings
The Central and Regional Governments may grant incentives to owners, users, and/or management of Smart Buildings as an effort to support the development of Smart Buildings.
The incentives may be in the form of:
- ease of licensing fees and services;
- technical support and/or expertise, including in the form of technical advice and/or assistance from a Smart Building Expert for a pilot project;
- awards in the form of certificates, plaques, and/or tokens of appreciation;
- publication and/or promotion; and/or
- increasing human resource capacity.
In addition to the above, the incentive may also be in the energy conservation sector.
- Administrative Sanctions for Smart Buildings
In compliance with the fulfillment of technical standards and certification by an owner, user, and/or management of a Smart Building that is categorized as mandatory may result with subject to administrative sanctions as stipulated under Article 44 of Regulation 10/2023.
In general, the administrative sanctions for technical planning, construction, utilization, and demolition are written warnings (up to three times). Additionally, for the technical planning stage, the administrative sanction may be in the form of delaying the issuance of building approvals, and for the utilization stage, the administrative sanctions may also be in the form of delaying the issuance of a certificate of occupancy extension and revocation of a Smart Building's certification status.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.

