Georgia's tax reforms over the past decade have created a competitive environment, making it an attractive destination for both local and international IT companies. Explore the benefits of Georgia's Small Business Tax Status and Virtual Zone Status for IT services. Understand eligibility criteria, tax obligations, and advantages for IT businesses and professionals. Maximize tax savings and operational efficiency with Georgia's favorable tax regimes and Eurofast as a reliable partner in your business endeavors.
ADVANTAGES OF SMALL BUSINESS TAX STATUS:

Types of IT Services Covered by the Small Business Status:
- activity in the field of computer programming
- computer hardware management
- Other activities in information technology and computer services.
Total Income Limit:
The total income from this type of activity during the calendar year must not exceed 500,000 GEL. Income earned for providing consulting services in the IT sector is not covered under Small Business Status and is subject to income tax at a rate of 20%.
How to Obtain the Small Business Status:
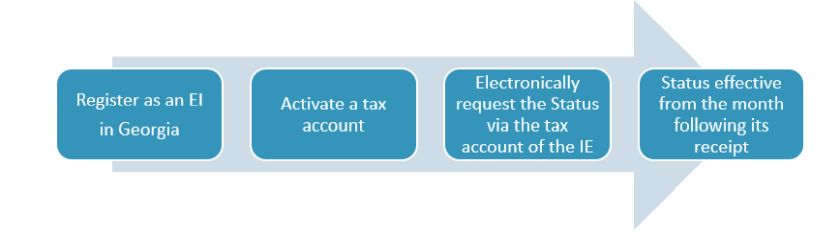
To obtain this status it's necessary to register as an Individual Entrepreneur (IE) in Georgia, activate the tax account and electronically request the small business status through the tax account of the IE. The Small Business Status becomes effective from the month following its receipt.
Tax Declaration and Payment Obligations:
- Submit a monthly tax declaration for income tax electronically by the 15th day of the following month.
- Pay the income tax as declared.
- Income exceeding 500,000 GEL within a calendar year is taxed at 3%.
- Exceeding the income limit twice in consecutive years results in the loss of Small Business Status for the following calendar year.
VAT Implications:
Services provided by an IT specialist to a Georgian client constitute turnover for VAT purposes. In case such income exceeds the limit of 100,000 GEL, an Individual Entrepreneur (IE) with Small Business Status will have an obligation to pay VAT on the amount exceeding the limit, in addition to paying income tax at the established rate.
ADVANTAGES OF VIRTUAL ZONE (VZ) STATUS:

Types of IT Services Covered by the VZ Status:
Information technologies, including the study, support, development, design, production, and implementation of computer information systems, resulting in the creation of software products.
Obtaining the VZ Status:
To obtain the VZ status in Georgia, it is necessary to:
- Register the company in Georgia.
- Apply for VZ status with the Ministry of Finance of Georgia through the Financial-Analytical Service.
The Revenue Service, through order N 42644 issued on December 31, 2021, approved a methodical instruction that specifies crucial details related to legal entities operating within the virtual zone.
Requirements for Maintaining VZ Status:
- The service (or software product) must be actually provided (software product – created) in Georgia and exported abroad, since remote work of employees outside Georgia threatens the loss of status and tax benefits.
- If there are no employees in the company's staff and the service is provided by the director, as a partner of the company, he/she can withdraw the company's income as dividends and thus use the tax incentive.
Tax Rates and Other Considerations:
- Withholding Tax on Services Used in Georgia: Income from services used in Georgia but obtained from foreign contractors (including foreign subscription services) without a permanent establishment in Georgia is subject to a 10% withholding tax rate (unless otherwise provided by a double taxation avoidance agreement).
- Income Tax on Employee Salaries: Employee salaries are subject to a 20% income tax rate.
- Property Tax: Property tax is calculated at 1% of the average market value of the property.
- VAT on Income from Georgian Sources: Income received from Georgian sources is subject to a 18% value-added tax (VAT). Companies must become VAT payers if their income from taxable VAT activities reaches 100,000 GEL within 12 consecutive months.
- Refundable VAT on Expenses Paid to Non-Residents: Expenses paid to non-residents of Georgia (including foreign subscription services) without a permanent establishment in Georgia are subject to refundable VAT at a rate of 18%. However, there is an option not to pay the accrued VAT if these services are used to provide primary services abroad.
In summary, Georgia's Small Business Tax Status and Virtual Zone Status provide significant tax advantages and operational flexibility for IT professionals and companies. With favorable tax regimes and a supportive business environment, Georgia stands out as a prime destination for IT businesses globally.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.

