This edition of the Automotive Industry Spotlight will focus on AI's use cases and potential impacts on the entire automotive value chain for automakers and suppliers looking to modernize their operating models.
In industry news, Honda announced it will double down on its investment in electric vehicles (EV) as it laid out plans for development between now and 2030. The International Union, United Automobile, Aerospace and Agricultural Implement Workers of America (UAW) is protesting the results of the vote it lost at a Mercedez-Benz plant in Alabama, citing the automaker's participation in union-busting activities. Nissan announced a major investment in advanced manufacturing, looking to improve its production output and quality control.
In regulatory news, an investigation into robotaxi startup Waymo continues to find further self-driving vehicle incidents, per the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA). A U.S. District Judge ruled that Tesla would not be able to dismiss class action claims related to alleged false advertising of its own self-driving software. Ford's planned recall for a fuel injector leak is under investigation for adequate safety practices and to determine whether its solution addresses the relevant issues.
Industry Focus — The Case for Artificial Intelligence in Automotive
Artificial Intelligence in the Automotive Industry
Artificial intelligence is projected to be a $184 billion global market in 2024, with future growth leading to a total market size of more than $850 billion by 2030. Industrial robotics and autonomous sensors will represent more than $200 billion of that total global market.1 While AI remains in its relative infancy for applications and product development, its use cases for the automotive industry have already manifested in meaningful ways across the entire automotive value chain.
Global growth potential aside, AI represents a significant opportunity for automakers and suppliers to radically change their operating models in every vertical, from the design and manufacturing process to actual consumer transportation and even down to service department vehicle maintenance.
Manufacturing Capabilities
The automotive industry was among the earliest adopters to implement predictive AI in its manufacturing processes. Simple processes like data sorting, analytics for equipment performance and production scheduling enabled significant productivity boosts. With the exponential advances in AI technologies in recent years, AI has become a critical part of most automakers' and suppliers' processes.1
The very near future of AI in automotive will start with vehicle design; automakers like Toyota are already using generative AI programming to influence vehicle design for aerodynamics, chassis dimensions and known engineering constraints to reduce the number of iterations in the vehicle design process.2 The processes have already led to performance output improvements in performance for the company's EV models.
Certain AI effects on the automotive manufacturing process will represent more direct benefit to bottom lines, including but not limited to:
- Equipment reliability: AI-fed vibration sensors can detect equipment function anomalies, diagnose issues and predict breakdown likelihood for heavy industrial equipment, enabling manufacturers to optimize production scheduling and maintenance planning.
- Quality control: AI-driven visual quality control systems can reduce human error rates in components of quality control that require visual inspection, such as inspecting machined parts, paint and textured surfaces through machine learning feedback loops.
- Supply chain efficiency: Traditional forecasting systems are currently dependent on human capabilities to sort through massive amounts of data and are heavily influenced by the rapidly growing number of hard-to-predict macroeconomic factors. Machine learning algorithms backed by AI can help make faster sense of data and external events to enable better — and even fully-automated — forecasting decision making, leading to potentially significant reductions in forecasting errors.
Transportation capabilities
While not without controversy, AI is already making a significant impact in actual consumer transportation. Self-driving robotaxi upstarts like Waymo are built on machine learning AI technology, leveraging external environmental data to adapt to surroundings and react accordingly. Tesla is notably on the leading edge for original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) developing self-driving with AI as a key technology pillar for the company.
In-vehicle consumer experiences are also ready to be heavily influenced by AI. Route optimization driven by real-time traffic pattern analysis leads to improved travel times for drivers. EV battery analysis can improve charging schedules, route optimization for charging networks and improved vehicle performance. Advanced driver security systems such as lane departure tracking, autonomous braking in emergency situations and adaptive cruise control have already led to significant increases in vehicle safety rates.
AI's full impact on transportation will continue to evolve over the coming years — and not without intense regulatory scrutiny. In recent weeks, the U.S. Department of Transportation's Advanced Research Projects Agency for Infrastructure (APRA-I) announced it would be further investigating the applications of AI in transportation, including risks, barriers to adoption and software development challenges. The agency cited its belief that "AI has the potential to transform transportation and mobility" but noted the risk of "tremendous peril if it is misapplied."3
Service and Maintenance
Similarly to the enhancements AI has already delivered to equipment reliability in automotive manufacturing processes, maintenance harnesses and sensors built into vehicles continuously monitor the part performance of components like engines, tires, brakes and transmission for the detection of patterns to predict failures well before they even occur.
With real-time component data analysis, vehicle issue diagnostics will be significantly enhanced. Rapid detection of error codes, recognition of fault patterns and identification of proper corrective actions will drastically improve service delivery. In the near-term, these benefits will lead to decreased vehicle downtime, service department and consumer cost savings and efficiency in maintenance plans. In the long-term — and on a much larger scale — predictive maintenance can improve automaker planning and execution for recalls, leading to significant cost saving opportunities and consumer safety improvements.
Industry Focus sources
Additional May insights are included below.
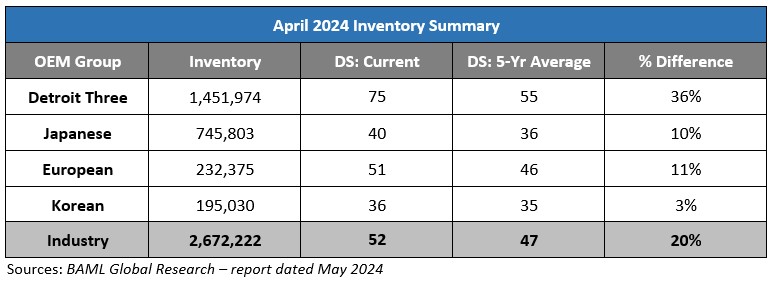
Industry Update
April inventory levels ended at 2.67 million units, a 9,000-unit increase from March. Days' supply closed at 52, approximately 20 percent above the five-year average. Inventory at the Detroit Big Three led the way for the U.S., with a 69,000-unit increase in inventory driven by a 36,000 unit increase for Stellantis.
Regulatory Landscape
NHTSA Investigation Finds Further Incidents with Waymo: An investigation into Alphabet's Waymo self-driving vehicles found an additional nine incidents related to the self-driving robotaxis, on top of the initial 22 that were reported to the NHTSA. The incidents in question "involved collisions with clearly visible objects that a competent driver would be expected to avoid,"1 and the NHTSA has given Waymo a deadline of June 11 to respond to a series of investigative questions.
Tesla Self-Driving Class Action Suit: A U.S. judge rejected Tesla's attempt to dismiss a class action lawsuit against the company for misleading claims that vehicles could have self-driving capabilities. The nationwide class action suit accuses the company of falsely advertising its autopilot feature, with a U.S. District Judge ruling owners could pursue negligence and fraud-based claims to the extent they relied on Tesla's representations of the features.
NHTSA Investigation into Ford Recall Safety: The NHTSA announced it had "significant safety concerns" with Ford's recall of more than 42,000 Bronco Sport and Escape models related to fuel injectors that might crack and leak fuel, potentially leading to under-hood fires. The company proposed an engine control software update rather than replacing the fuel injectors, which the NHTSA said "does not address the root cause of the issue."1
Regulatory News source
1. Automotive News
Originally published 30 May 2024
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.




