The Fast-Moving Consumer Goods (FMCG) sector is a cornerstone of the Indian economy, providing essential products to millions of consumers. However, like any industry, it is not immune to financial instability. The insolvency of a major FMCG company can have a devastating ripple effect throughout the entire supply chain, severely impacting distributors, retailers, and even contract manufacturers who rely heavily on them.
Distributors and retailers face the immediate impact of product shortages, revenue loss, and potential reputational damage. Contract manufacturers, particularly those heavily reliant on the insolvent company, also bear the brunt of the disruption. This article explores the challenges arising from FMCG company insolvencies and offers proactive strategies for distributors, retailers, and contract manufacturers to mitigate their risks.
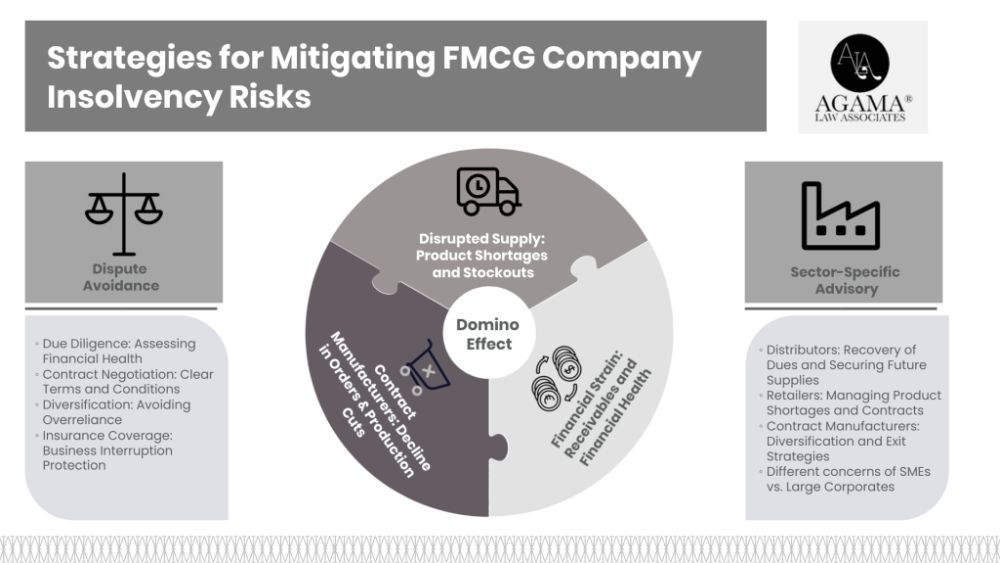
The Domino Effect: How FMCG Insolvency Impacts the Supply Chain
When a large FMCG company becomes insolvent, the consequences are far-reaching:
- Disrupted Supply: Distributors and retailers suddenly face product shortages, leading to stockouts and lost sales opportunities.
- Financial Strain: Distributors may have outstanding receivables from the insolvent company, jeopardizing their own financial health.
- Uncertainty for Contract Manufacturers: Contract manufacturers heavily reliant on a single insolvent FMCG company may experience a significant decline in orders, potentially leading to production cuts or even closure.
International Considerations: Cross-Border Disputes and Strategies
The globalization of supply chains means that FMCG company insolvencies can create a ripple effect across borders. Indian distributors and retailers sourcing products from foreign FMCG companies face unique challenges.
- Governing Law and Jurisdiction: Cross-border supply contracts often contain clauses specifying the governing law and jurisdiction for dispute resolution. Businesses need to carefully consider these clauses to understand their legal rights and forum for resolution in the event of an insolvency.
- Recognition of Foreign Insolvency Proceedings: The Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC) of India includes provisions for the recognition of foreign insolvency proceedings. It is vital to consult with legal experts to navigate the complexities of cross-border insolvency and secure the best interests of the business.
- Monetization Opportunities: Cross-border disputes provide Indian lawyers with opportunities to monetize their expertise. Understanding the legal nuances of both Indian and relevant foreign jurisdictions positions them to offer valuable guidance to businesses navigating these complex situations.
Risk Management Strategies: Proactive Steps to Mitigate Disputes
Taking proactive measures can significantly minimize the impact of FMCG insolvency on distributors and retailers:
- Due Diligence: Thoroughly assess the financial health and reliability of FMCG companies before entering into long-term agreements. Monitor their financial reports and credit ratings for any red flags.
- Contract Negotiation: Carefully draft contracts with clear terms and conditions addressing potential insolvency scenarios. Include clauses for early termination, alternative supply arrangements, and the return or sale of unsold inventory.
- Diversification: Avoid overreliance on a single FMCG supplier. Maintain relationships with multiple suppliers to mitigate the risk of complete disruption in case of insolvency.
- Insurance Coverage: Explore business interruption insurance policies that can provide financial protection in case of supply chain disruptions due to FMCG insolvencies.
Business Regulatory Advisory
The regulatory landscape governing distribution and retail in India is constantly evolving. Here are critical areas for industry professionals to stay aware of:
- Competition Law: The Competition Act of India prohibits anti-competitive agreements and abuse of dominant market positions. Businesses should be mindful of these provisions to avoid legal complications.
- Consumer Protection: The recent Consumer Protection Act, 2019 strengthens consumer rights in India. Distributors and retailers need to ensure compliance with provisions regarding product quality, warranties, and unfair trade practices.
- E-commerce Regulations: The burgeoning e-commerce sector in India comes with specific regulations governing online platforms and sellers. Businesses expanding into online channels need to familiarize themselves with these rules.
Adapting to the Needs of Industry Professionals
The legal challenges faced by distributors, retailers, and contract manufacturers in the FMCG sector necessitate tailored solutions. Here's a breakdown of how legal counsel can assist different stakeholders:
Distributors
- Recovery of Dues: Filing claims with the insolvency resolution professional to maximize the recovery of outstanding debts from the insolvent FMCG company.
- Securing Future Supplies: Advising on strategies to diversify supplier base, renegotiate existing contracts, or establish new agreements with alternative FMCG companies.
- Contingent Liabilities: Assessing potential liabilities arising from product defects or consumer complaints linked to the insolvent company's products.
Retailers
- Product Shortages and Consumer Disputes: Guidance on managing customer expectations, sourcing alternative products, and handling potential consumer disputes arising from product scarcity or quality issues.
- Contractual Obligations: Reviewing contracts with the insolvent FMCG company for clauses addressing termination due to insolvency or the right to source similar products elsewhere.
- Protection of Margins: Negotiating with alternative suppliers to ensure competitive pricing and maintain profitability during disruptions.
Contract Manufacturers
- Diversification of Client Base: Assisting in identifying new buyers and expanding the client portfolio to reduce reliance on a single FMCG company.
- Enforceability of Contracts: Analyzing existing contracts for clauses protecting against sudden order cancellations or breach due to insolvency.
- Negotiating Exit Strategies: Advising on potential options for terminating agreements, mitigating losses, and negotiating favorable settlement terms with the insolvent FMCG company.
Concerns of SMEs vs. Large Corporates
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) often face greater vulnerabilities in the aftermath of an FMCG insolvency compared to large corporations. Legal counsel should be sensitive to these differences:
- SMEs: Focus on immediate survival strategies, cash flow management, swift recovery of dues, and assistance in finding alternative buyers or suppliers.
- Large Corporations: Emphasize long-term risk management strategies, diversification of supply chains, and robust contract drafting to minimize future exposure.
Delivering Tailored Solutions for Diverse Sectors
The FMCG sector encompasses a wide range of products, from food and beverages to personal care and household goods. Specific legal needs can vary based on the sub-sector. Industry professionals should seek counsel with expertise in areas like:
- Food and Beverage: Compliance with food safety regulations, product labeling laws, and managing potential product liability claims.
- Personal Care and Cosmetics: Understanding regulations, product safety standards, and intellectual property protection (trademarks, patents).
- E-commerce and Direct-to-Consumer: Legal considerations for online sales platforms, consumer protection laws, and logistics contracts.
Conclusion
The insolvency of a major FMCG company can have a profound impact on the entire supply chain. Distributors, retailers, and contract manufacturers must be proactive in mitigating risks and protecting their business interests. By implementing sound risk management strategies, diversifying their portfolios, and seeking expert legal guidance, industry professionals can navigate the challenges posed by FMCG insolvencies and emerge stronger.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.
We operate a free-to-view policy, asking only that you register in order to read all of our content. Please login or register to view the rest of this article.


